A) Type and adjustment of bench nozzles:
Bench nozzle: DN12SD12 (NIPPONDENSO)
Spray needle opening pressure: 145-155 bar
b) Bench tachometer error:±40 rpm.
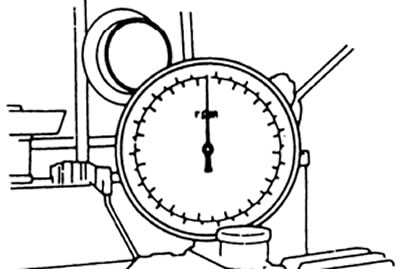
V) Set the bench dial to zero.
G) Install the pump on the stand.
Reminder: Mark the coupler against the pump shaft key.
d) High pressure pipes:
- Outer diameter - 6.0 mm
- Inner diameter - 2.0 mm
- Length - 840 mm
- Minimum bending radius - 25 mm
e) Connect bench tubes of a supply and removal of fuel. Install adapters if necessary.
Attention: fasten the fuel outlet pipe only with the pump bolt (bolt with jet, marking OUT).
and) Remove the right cover of the advance machine.
h) Install the plunger stroke measurement tool. (NIPPONDENSO No. 95095-10220 and 95095-10231).
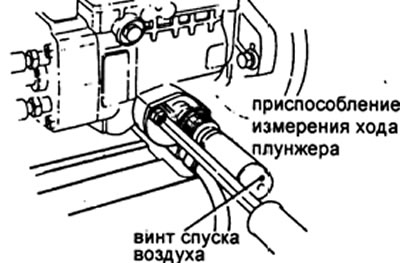
And) Apply +12V to the fuel cut-off valve (from stand system or battery).
To) The fuel supply pressure to the pump must be 0.2 bar. The temperature of the fuel during testing should be 40 - 45°C.
l) Install the protractor on the injection pump lever.
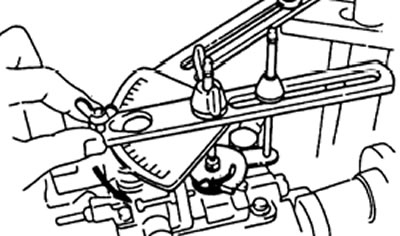
m) Lock the pump control lever in the maximum speed position.
n) Check the correct orientation of the cam (correct assembly):
Remove the nozzle pressure valve "WITH".
Align the key position mark on the coupling with the fitting "WITH". Turn on the booster pump of the stand. If fuel does not flow from port C, disassemble the pump and change the position of the cam by 180°.
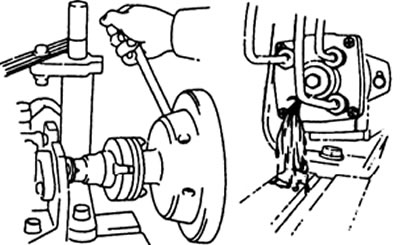
O) Set the pump to 1200 - 2000 rpm for 5 minutes. Check for fuel leaks and unusual noise.
2. Pre-setting of cyclic feed at full load.
A) Set the injection pump control lever to the maximum position. On a supercharged engine, apply pressure to the corrector:
Without height compensator 0.65±0.02 bar
With height compensator - 1.16 bar
b) Measure the amount of fuel supplied. (See table. 1)
Table 1
| engine's type | Rotation frequency, rpm | The number of cycles | Fuel volume, cm3 |
| 2L | 1200 | 200 | 10,0-10,5 |
| 2L-T (with height compensator) | 1400 | 200 | 14,0-14,3 |
| 2L-T (rest) | 1200 | 200 | 14,0-14,3 |
| 3L | 1200 | 200 | 11,0-12,0 |
| 1KZ-T without height compensator | 1800 | 200 | 15,4 -15,8 |
| 1KZ-T with height compensator | 1800 | 200 | 14,5-14,9 |
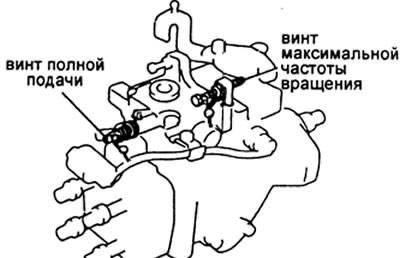
V) Remove the O-ring from the maximum feed screw (the seal is welded by turning welding) or cut the wire of a conventional seal.
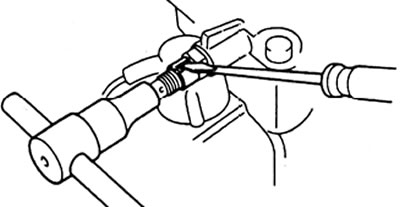
d) Adjust the cyclic feed by turning the full feed screw.
Note: The cycle feed will increase by about 3cm3/200 cycles for every 1/2 turn of the screw.
3. Preliminary adjustment of the load injection advance controller.
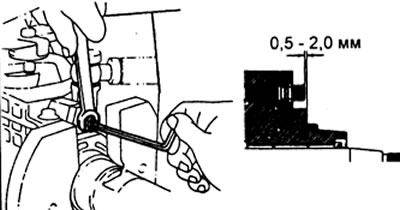
Install the governor shaft outlet.
Shaft output - 0.5-2.0 mm
4. Presetting the maximum speed.
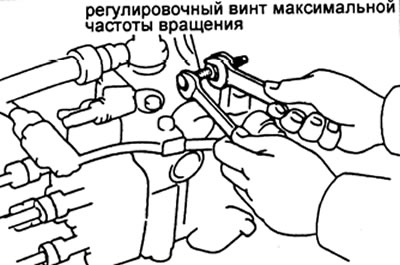
A) Set the control lever to the maximum speed stop.
b) (2L-T) Apply a pressure of 0.63±0.02 bar to the boost corrector.
V) (1KZ-T)
- With a power control drive, apply a vacuum of 0.67 bar to the drive.
- without height compensator: apply a pressure of 0.67 bar to the boost corrector.
- with height compensator: apply a pressure of 1.16 bar to the boost corrector.
G) (All models) measure fuel delivery (see table. 2)
d) Remove the seal from the maximum speed screw.
e) Adjust the cyclic feed by turning the screw.
5. Pressure adjustment of the booster pump.
A) Measure the pressure in the pump housing.
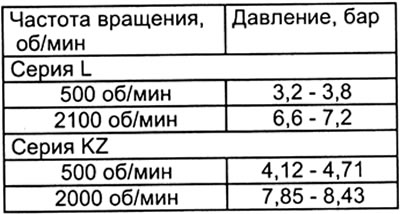
b) If the pressure is low, then adjust it with light strokes on the piston of the pressure reducing valve, controlling the pressure gauge readings.
Attention: if the pressure is too high or the pressure reducing valve spring preload is maximum, replace the pressure reducing valve.
6. Checking the fuel consumption for return to the tank.
Measure return fuel consumption:
Series L
- 70 - 380 cm3/min at 2200 rpm
KZ series
- 720 - 1150 cm3/min at 500 rpm
Caution: always install the fuel return pipe mounting bolt (with jet and OUT mark), belonging to the pump.
7. For the following adjustments, turn off the engine warm-up control (if installed).
A) Turn the heat control lever 20°counterclockwise.
b) Place a metal plate 8.5 - 10 mm thick between the lever and thermostat plunger.
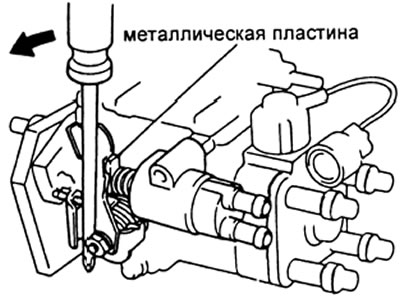
Table 2
| engine's type | Speed rpm | The number of cycles | Fuel volume, cm3 |
| 2L, 2L-T | 2450 | 200 | 4,0-5,6 |
| 3L | 2400 | 200 | 4,6-6.2 |
| 1KZ-T | 2300 | 200 | 5,2 - 7,2 |
8. Adjustment of the automatic injection advance.
A) Set the measuring device to zero.
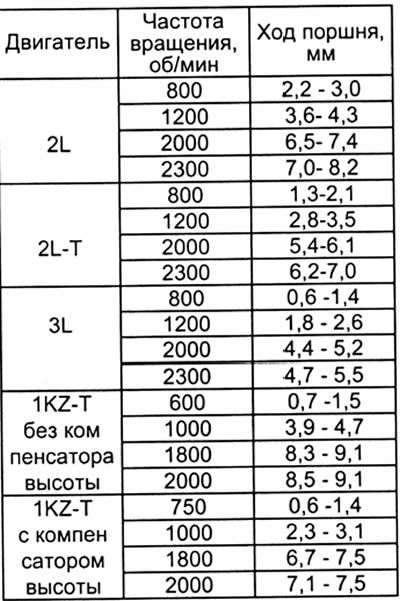
b) Measure the stroke of the automatic advance piston at the following speeds.
(2L-T)
Apply a pressure of 0.63±0.02 bar to the boost corrector.
(1KZ-T)
- (With power control drive). Create a vacuum of 500 mm Hg on the drive.
- (without height compensator). Apply a pressure of 0.67 bar to the boost corrector.
- (With height compensator). Apply a pressure of 1.16 bar to the boost corrector.
Attention: the hysteresis should not be more than 0.3 mm.
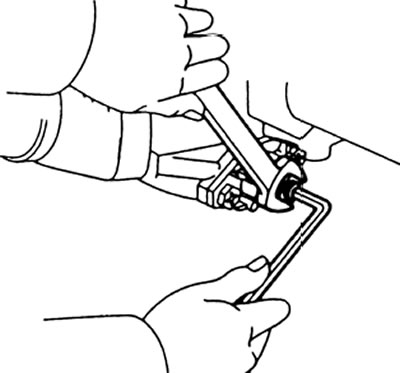
V) Use a 5mm Allen key to adjust the stroke of the injection advance plunger.
Note: Plunger travel decreases when the screw is turned clockwise and increases when the screw is turned counterclockwise.
G) (Engine 1KZ-T) Check the characteristics of the machine.
If the characteristic differs from the specified one, select and replace the internal spring.
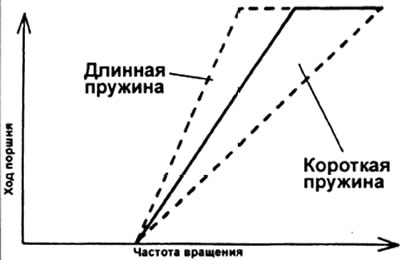
Free length of the spring - 40.4 mm; 39.5 mm; 38.8mm; 38.2 mm
Note: The stroke of the automatic advance piston increases with the lengthening of the spring.
9. (2L-T and 1KZ-T) Checking the tightness of the boost corrector.
A) Apply 1.36 bar pressure to the corrector.
b) In 10 seconds, the pressure should not fall below 1.33 bar.
10. Adjustment of cyclic feed at full load.
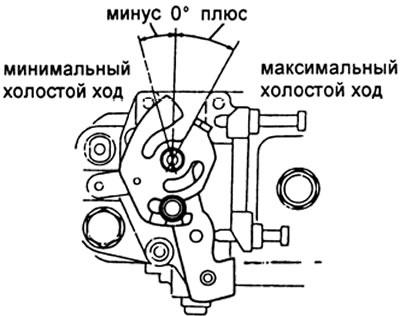
A) Rotary angle of the regulator lever: all models plus 23 - 33 degrees, minus 13 - 22 degrees.
b) (2L-T) Apply a pressure of 0.63±0.02 bar to the boost corrector.
(1KZ-T)
- (With power control drive). Apply a vacuum of 0.67 bar to the drive.
- (without height compensator). Apply a pressure of 0.67 bar to the boost corrector.
- (With height compensator). Apply a pressure of 1.16 bar to the boost corrector.
V) Measure the injected fuel delivery at full load.
| Engine | Rotation frequency, rpm | feed cm3 |
| 2L | 1200 | 10,2-10,7 |
| 2L-T | 1200 | 14,0-14,3 |
| 3L | 1200 | 11,5-12,0 |
| 1KZ-T* | 1800 | 15,4-15,8 |
| 1KZ-T** | 1800 | 14,5-14,9 |
* without height compensator
** with height compensator
G) Adjust by turning the full feed screw.
Note: The feed will increase by about 3cm3/200 cycles for every 1/2 turn of the screw.
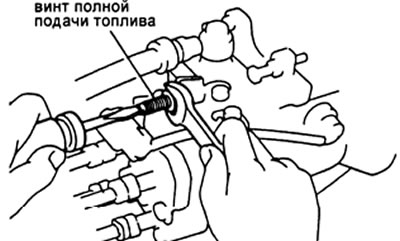
(Only for 1KZ-T)
d) Relieve the vacuum from the power control actuator and re-measure the fuel delivery.
| Engine | Rotation frequency, rpm | feed cm3 |
| 1KZ-T* | 1200 | 14,6-14,9 |
| 1KZ-T** | 1200 | 14,5-14,8 |
* without height compensator.
** with height compensator.
d) Adjust the feed with the drive stop screw.
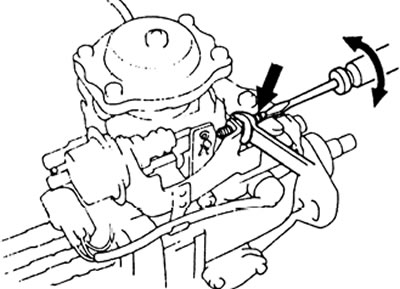
e) Apply a vacuum of 500 mm Hg to the actuator. and check for clearance (3 mm or more) between screw and drive lever.
10. Feed adjustment at maximum idle speed.
(2L-T)
Apply a pressure of 0.63 + 0.02 bar to the boost corrector.
(1KZ-T)
- (With power control drive). Create a vacuum of 500 mm Hg on the drive.
- (without height compensator). Apply a pressure of 0.67 bar to the boost corrector.
- (With height compensator). Apply a pressure of 1.16 bar to the boost corrector.
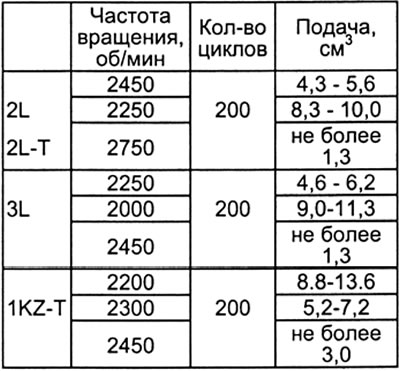
A) Adjust by turning the maximum speed screw.
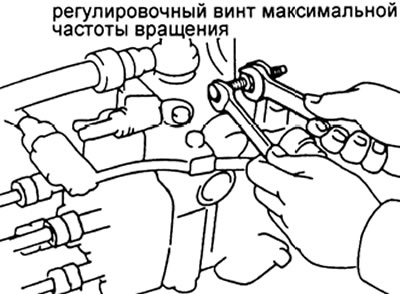
Adjustment of giving on the external characteristic.
(2L-T)
- Apply a pressure of 0.63±0.02 bar to the boost corrector.
Adjustment of giving on the maximum frequency of rotation of idling.
(1KZ-T)
- (with power control drive) create a vacuum of 500 mmHg on the drive.
Permissible feed unevenness
| Rotation frequency (rpm) | unevenness (cm3) |
| 1200- 1400 | 0,4 |
| 100 | 1,2 |
| 500 | 0,5 |
| 1950-2100 | 0,5 |
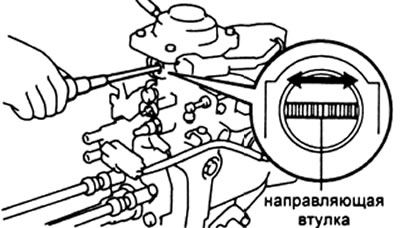
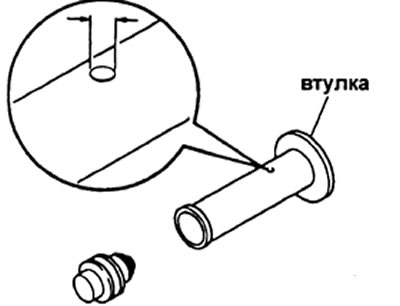
If the starting feed value (at 100 rpm) does not match the table value, replace the regulator bushing plug. Press the plug out of the regulator bushing.
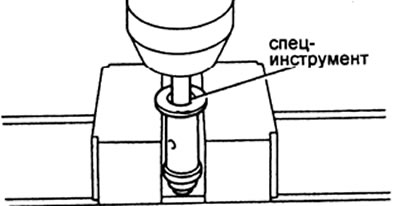
Remove:
- (11 retaining ring;
- (2) spacer;
- (31 thrust bearings;
- (4) cork.
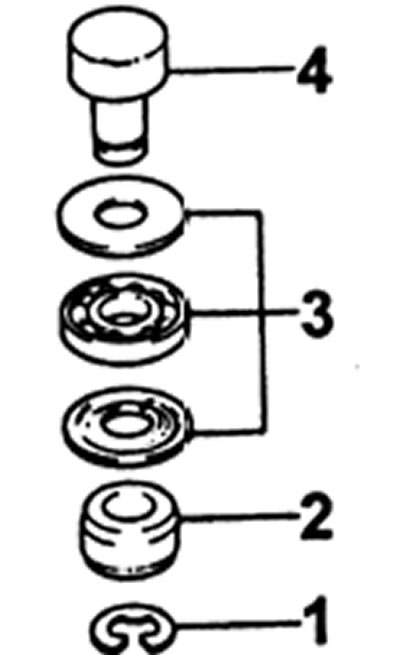
Measure the thickness of the bushing plug head, select a new bushing plug. Note: lengthening the plug by 0.1 mm increases the starting feed by 0.6 cm3/200 cycles. If the supply unevenness exceeds the specified value, then replace the discharge valve.
Stoppers are produced with a head thickness from 3.0 to 4.2 mm in 0.1 mm increments.
Assemble the regulator bushing in the reverse order of disassembly, press the plug into the bushing.
12. Minimum feed rate adjustment at full load.
a) (2L-T) On the boost corrector, create a vacuum of 200 mm Hg. (1KZ-T)
- (with power control drive) create a vacuum of 500 mmHg on the drive.
- (without height compensator) release the pressure on the boost adjuster.
- (with height compensator) apply a pressure of 0.46 bar to the boost corrector.
b) Measure the fuel supply.
| Rotation frequency, rpm | Number of cycles | Submission, cm3 |
| 1400 (2L-T) | 200 | 8,8-10,0 |
| 500 (2L-T) | 200 | 10,6-11,4 |
| 500 (1KZ-T) * | 200 | 11,9-12,5 |
| 500 (1KZ-T) ** | 200 | 8,1-9,3 |
* without height compensator
** with height compensator
V) The feed change is carried out either by replacing the spacer (washers B, pre-injection engine), or by turning the stop of the stroke limiter of the corrector rod.
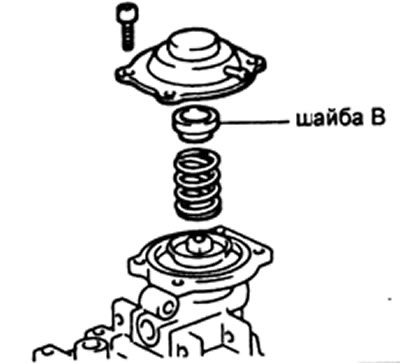
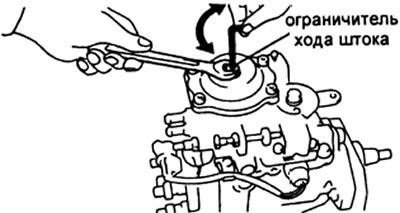
13. Adjustment of the characteristics of the boost corrector.
(2L-T)
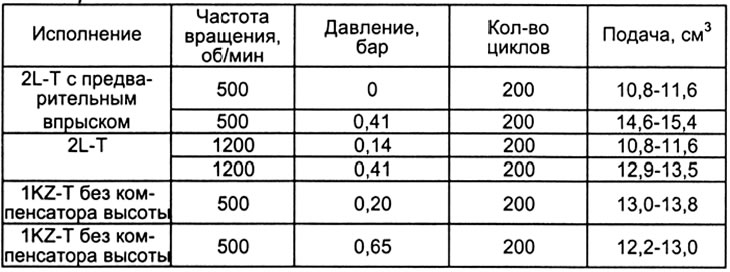
A) Apply pressure to the corrector according to table 3.
(1KZ-T)
- (With power control drive) create a vacuum of 500 mmHg on the drive.
- (without height compensator) apply a pressure of 0.20 bar to the boost corrector.
- (With height compensator) apply a pressure of 0.65 bar to the boost corrector.
G) Measure fuel delivery and compare with table 3 (see next page).
b) Measure fuel delivery and compare with table 3 (see next page).
V) Adjust the fuel supply by turning the corrector rod guide bush (turning clockwise increases feed).
G) On the 1K2-T engine pump, remove the rubber cap, corrector drain screw and sealing washer.
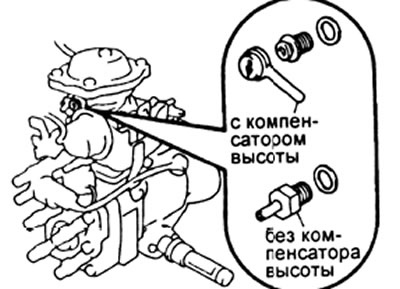
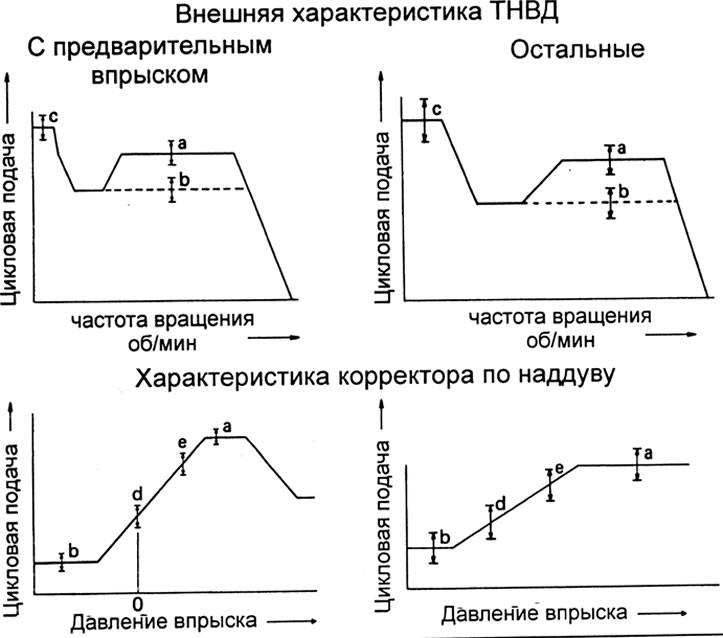
Table 3
14. (2L-T, 1KZ-T) Checking and adjusting the slope of the boost corrector characteristic.
A) With power control: create a vacuum of 500 mmHg on the drive
b) Pressurize the corrector.
V) Measure the fuel delivery and compare with the external data table
G) (with pre-injection). Correction of the inclination of the characteristics of the corrector is carried out by replacing the spring.
Spring rate: 1.2 and 1.4 kg/cm
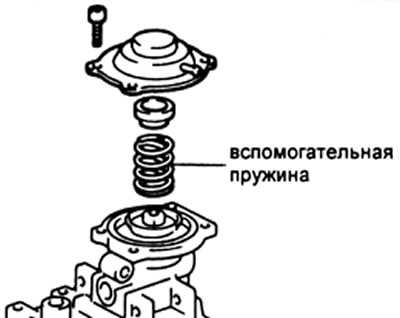
15. (2L-T, 1KZ-T) Hysteresis check. Compare the cyclic fuel supply when the pressure on the corrector increases from 0 to 0.74 bar and when the pressure decreases from 0.74 bar to 0.
Take measurements at 500, 1200 and 1400 rpm. The maximum deviation in fuel supply in similar modes should not exceed 0.3 cm3/200 cycles. If there is an increased hysteresis, check the quality of the assembly of the corrector and the presence of a sufficient amount of lubricant.
16. Adjustment of automatic injection advance (by load).
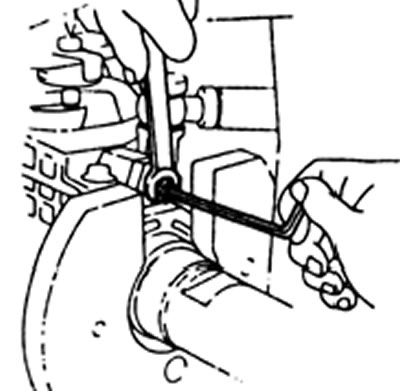
A) Adjustment is carried out by turning the shaft of the regulator sleeve. The beginning of the operation of the machine at a speed of 1200 rpm (L-series) or 1000 rpm (KZ-series).
b) Move the control lever to the maximum speed position and measure the amount of fuel supply.
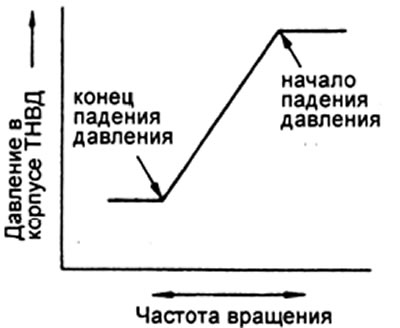
V) Slowly move the lever towards the minimum idle stop and secure the lever at the point where the pressure in the pump housing begins to drop.
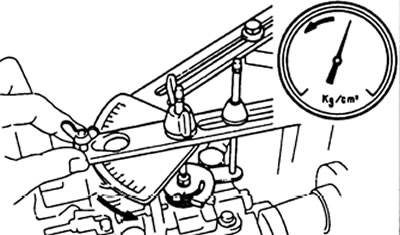
G) Measure the flow at the point where the pressure drop begins. Calculate the difference in feeds and compare with the data in the table.
| Engine | Rotation frequency, rpm | Number of cycles | Feed difference, cm3 |
| 2L- (T) | 1200 | 200 | 0,2-1,0 |
| 3L | 1200 | 200 | 0,6-1,4 |
| 1KZ-T | 1000 | 200 | 0,2-1,0 |
d) Adjust the feed difference by turning the governor shaft
Note: half a turn of the governor shaft changes the feed by 3 cm3/200 cycles.
e) Move the control lever to the point where the pressure drop in the pump casing stops, secure the lever.
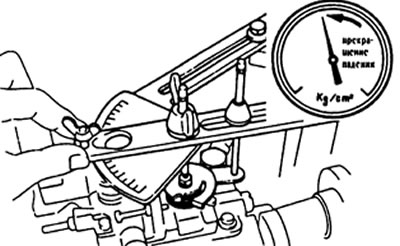
- Compare the amount of fuel supply with the data in the table.
| Engine | Rotation frequency, rpm | Number of cycles | Submission, cm3 |
| 2L | 1200 | 200 | 7.6-8.0 |
| 2L-T | 1200 | 200 | 8,1-8,5 |
| 3L | 1200 | 200 | 8,7-9,1 |
| 1KZ-T | 1000 | 200 | 10,2-10,6 |
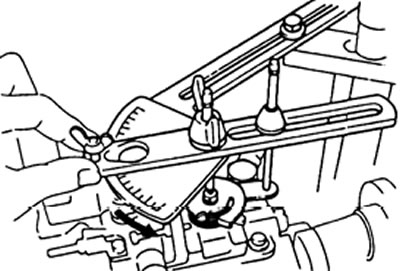
and) Check the change in stroke of the injection advancer plunger at the start and end points of the pressure change in the pump. Adjustment of the stroke of the plunger of the machine is carried out by replacing the bushing of the regulator (changing the diameter of the bushing holes). Increasing the diameter of the holes reduces the stroke of the plunger.
| Engine | Speed, rpm Difference in plunger travel, mm | |
| 2L-T | 1200 | 1,44-1,84 |
| 2L.3L | 1200 | 0,62-1,02 |
| 1KZ-T | 1000 | 1,44-2,24 |
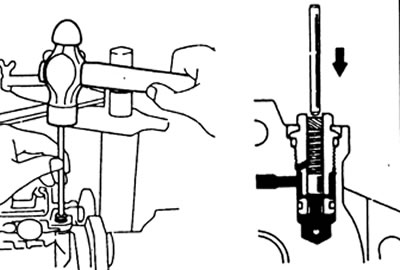
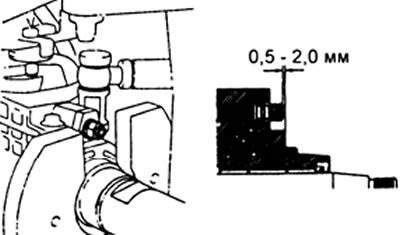
h) Measure the protrusion of the governor shaft.
Protrusion - 0.5-2.0 mm
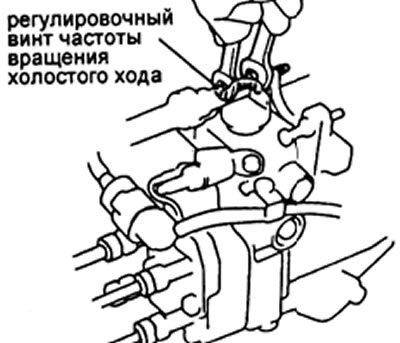
17. Adjusting the idle speed and checking the minimum speed controller (see table. 4)
- Adjust the feed by turning the minimum idle screw.
2L-T engines
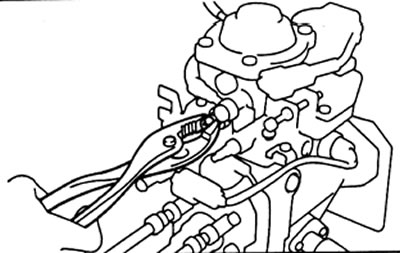
A) Use pliers to remove the load shedding retarder cap.
b) Completely unscrew the retarder adjustment screw.
V) Measure the cycle feeds according to table 5.
G) Adjust the feed by turning the minimum idle screw, d) Set the pump shaft speed to 600 rpm and move the control lever so that the fuel supply is 0.5-0.7 cm3/200 cycles.
e) Turn the retarder screw until the feed increases by 0.2-0.4 cm3/200 cycles.
and) Re-adjust the minimum idle speed by turning the stop screw according to table 6.
h) Install the retarder screw cap
Engines 1KZ-T
A) Use pliers to remove the load shedding retarder cap.
b) Completely unscrew the retarder adjustment screw.
- (With power control drive) Create a vacuum of 500 mm Hg on the drive.
(With height compensator) Apply a pressure of 0.49 bar to the boost corrector.
V) Pre-adjust the fuel supply by turning the minimum idle screw.
Speed - 1000 rpm
Feed q = 1.7 - 2.1 cm3/200 cycles
G) Retarder feed adjustment.
Adjust the feed by turning the retarder adjusting screw.
Speed - 1000 rpm
Feed q + 0.06 - 0.16 cm3/200 cycles
Table 4. 2L and 3L engines
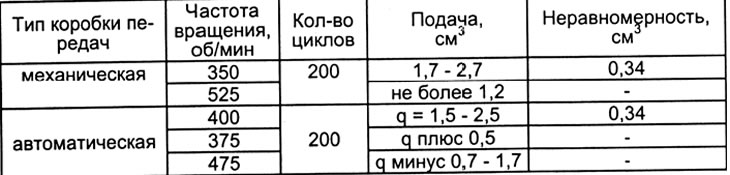
Table 5
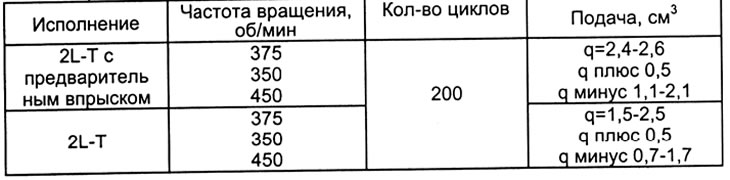
Table 6
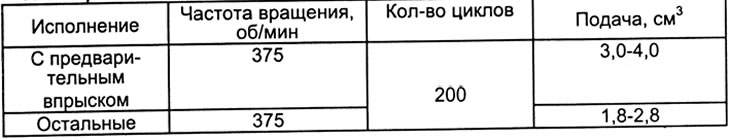
Table 7

e) Final idle adjustment.
Adjustment is carried out by turning the minimum idle screw.
Speed - 350 rpm
Feed 3.0 - 4.0 cm3/200 cycles
18. Adjustment of the advance angle during cold start.
A) Measure the temperature of the fuel at the pump.
Fuel temperature - 15 - 35°С
b) Install the pump shaft key vertically.
V) Set the injection advance plunger stroke meter to zero.
G) Set the pump control lever to the stop and take the angle of rotation of the lever as zero.
d) Delete (if installed) plate between the heating control lever and the thermostat.
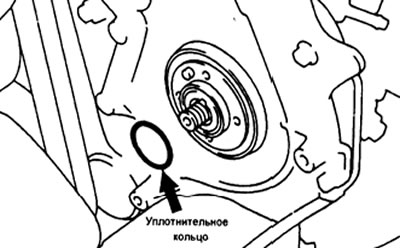
e) Turn the heating control lever clockwise to a torque of 5 Nm and hold the torque for 10 seconds.
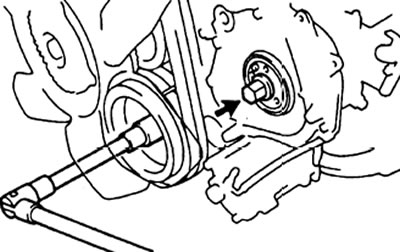
and) Measure advance plunger stroke (see table 7).
h) Adjust the plunger stroke by turning the adjusting screw.
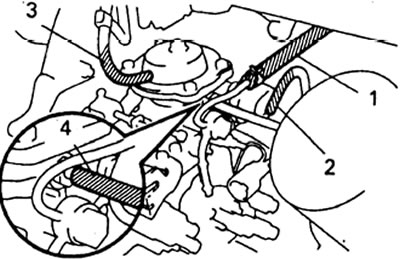
19. Adjustment of the heating control system.
A) Measure the clearance between the control lever and the minimum idle screw.
| Fuel temperature | Gap |
| 20°С | 6 mm |
| 50°C | 0 mm |
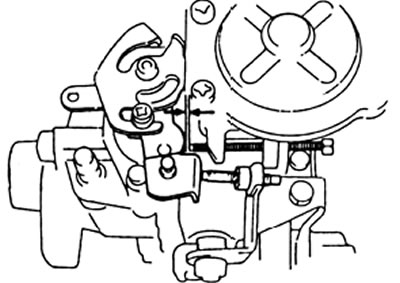
b) Adjust the gap by turning the screw in the heat control lever.
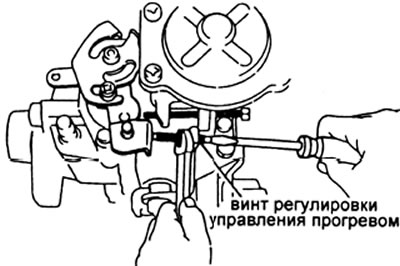
20. Install the seals on the screws for maximum speed and full fuel supply.