Attention! Use only a pointer voltmeter, as it is necessary to observe the oscillation of the pointer.
Cars have one or two oxygen sensors. On models with two sensors, the main oxygen sensor is installed in front of the catalyst and monitors the composition of exhaust gases not cleaned by the catalyst. An additional oxygen sensor monitors the composition of the exhaust gases after they have passed through the catalyst. Depending on the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, the sensor induces a voltage of 0.1 V (high oxygen, lean mixture) up to 0.9 V (low oxygen, rich mixture). Based on this data, the ECM changes the opening time of the fuel injectors and changes the fuel ratio in the fuel mixture.
The oxygen sensor does not induce any voltage when the sensor temperature is less than 315°C.
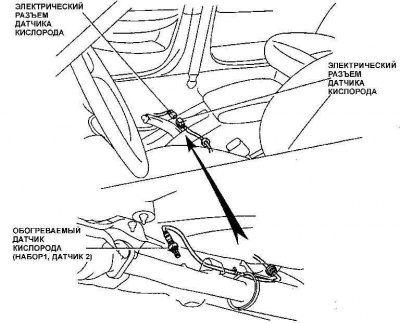
The front seat must be removed to access the rear oxygen sensor connectors.
Checking the performance of the oxygen sensor on six-cylinder engines
 | 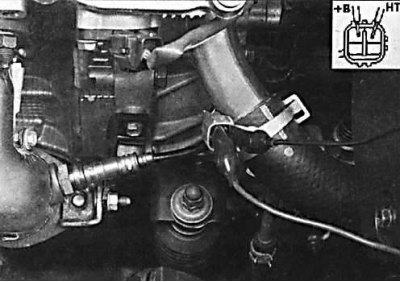 |
1. To test the oxygen sensor, disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor and connect an ohmmeter to the +B and NT terminals of the sensor connector. The resistance of the sensor should be in the range of 11-17 ohms. On models with four-cylinder engines, the oxygen sensor is connected with one wire. On models with six-cylinder engines with an oxygen sensor heater, the sensor is connected to a four-pin connector. Later models with four-cylinder engines have two oxygen sensors, while models with six-cylinder engines have three oxygen sensors. Block 1 sensor 1 and block 2 sensor 1 are located before the catalyst, and block 1 and sensor 2 are located after the catalyst. On models with six-cylinder engines, the front seat must be removed to access the rear oxygen sensor electrical connector.
2. Check the condition of the oxygen sensor heater circuit. When the ignition is switched on, there should be a voltage of 12 V at the connector pins (See table. "V6 engines 1992 and 1993", "V6 engines since 1994").

3. Check the voltage induced by the oxygen sensor. Connect one wire of the millivoltmeter to the electrical connector of the oxygen sensor, and connect the second wire to ground. Check the voltage created by the oxygen sensor on the contacts (See table. "Four-cylinder engines", "Six-cylinder engines 1992 and 1993", "Six-cylinder engines since 1994").
4. The value of the signal induced by the oxygen sensor on a cold engine is from 0.1 to 0.2 V, and after the engine warms up it ranges from 0.1 to 0.9 V.

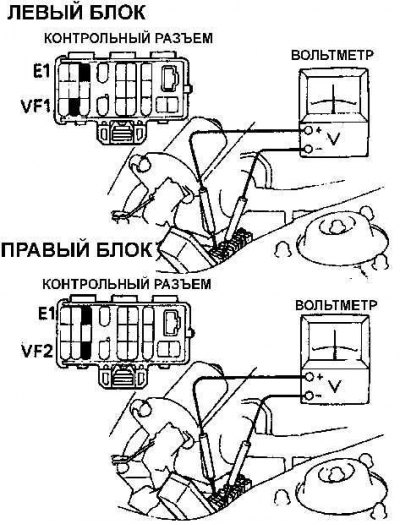
5. On models 1992 and 1993. Warm up the oxygen sensor to operating temperature and connect a pointer voltmeter to contacts VF1 and E1 of the control connector.
6. On six-cylinder engines, connect a pointer voltmeter to pins VF1 and E1 and pins VF2 and E1 to test the oxygen sensor (See fig. Checking the performance of the oxygen sensor on six-cylinder engines).
7. Start the engine and increase its speed to 2500 rpm for 2 minutes and then close the contacts TE1 and E1 of the control connector with an additional wire. Check that the voltmeter needle fluctuates 8 times in 10 seconds.
 |  |

8. To replace the oxygen sensor, remove the ground wire, raise the car, disconnect the connector from the sensor and unscrew the oxygen sensor.
V6 engines 1992 and 1993
| additional | black/orange wire (+) |
| oxygen sensor | brown wire (-) |
| main number 1 | not used |
| main number 2 | not used |
V6 engines since 1994
| block 1 sensor 1 | black/orange wire (+) brown wire (-) |
| block 2 sensor 1 | black/orange wire (+) brown wire (-) |
| block 1 sensor 2 | black/orange wire (+) brown wire (-) |
Four-cylinder engines
| master oxygen sensor | white wire |
| additional oxygen sensor | red/blue wire |
Six-cylinder engines 1992 and 1993
| main number 1 | white wire |
| main number 2 | red/blue wire |
| additional oxygen sensor | white wire |
Six-cylinder engines since 1994
| block 1 sensor 1 | white wire |
| block 2 sensor 1 | red/blue wire |
| block 1 sensor 2 | black wire |
